How long does menopause last? This question weighs heavily on the minds of many women as they approach this significant life transition. Join us on a journey to unravel the complexities of menopause, exploring its duration, stages, symptoms, and more.
From the onset of perimenopause to the years beyond, we’ll delve into the physical, emotional, and social implications of menopause. Along the way, we’ll uncover effective strategies for managing its symptoms and promoting overall well-being.
Duration of Menopause
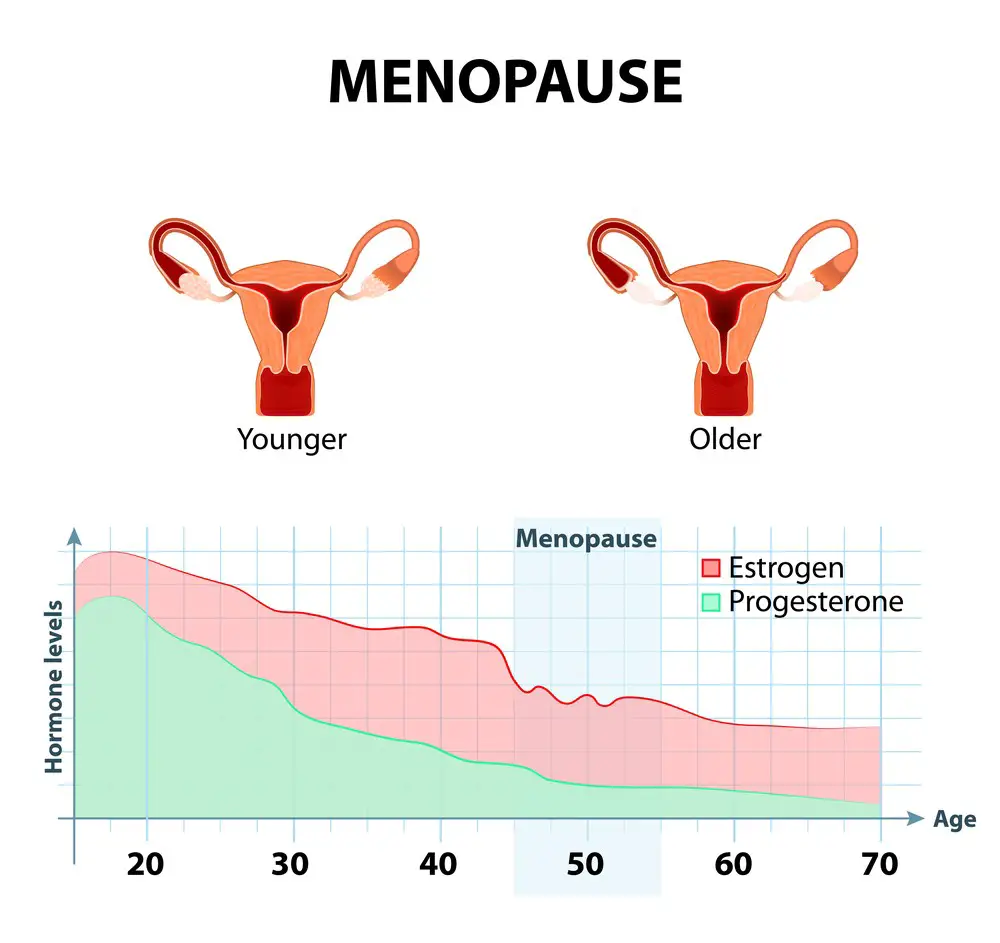
Menopause, the permanent cessation of menstruation, typically occurs between the ages of 45 and 55. The average age of menopause in the United States is 51 years. However, the duration of menopause can vary significantly from person to person.
Several factors can influence the length of menopause, including:
Age
Age is the most significant factor that determines the duration of menopause. Women who experience menopause at a younger age tend to have a shorter menopausal period than those who experience menopause at an older age.
Lifestyle
Lifestyle factors, such as smoking, alcohol consumption, and obesity, can also affect the duration of menopause. Smoking has been linked to an earlier onset of menopause, while alcohol consumption and obesity have been associated with a longer menopausal period.
Health Conditions
Certain health conditions, such as thyroid disease and diabetes, can also influence the duration of menopause. Women with thyroid disease tend to experience menopause at an earlier age, while women with diabetes tend to have a longer menopausal period.
Stages of Menopause
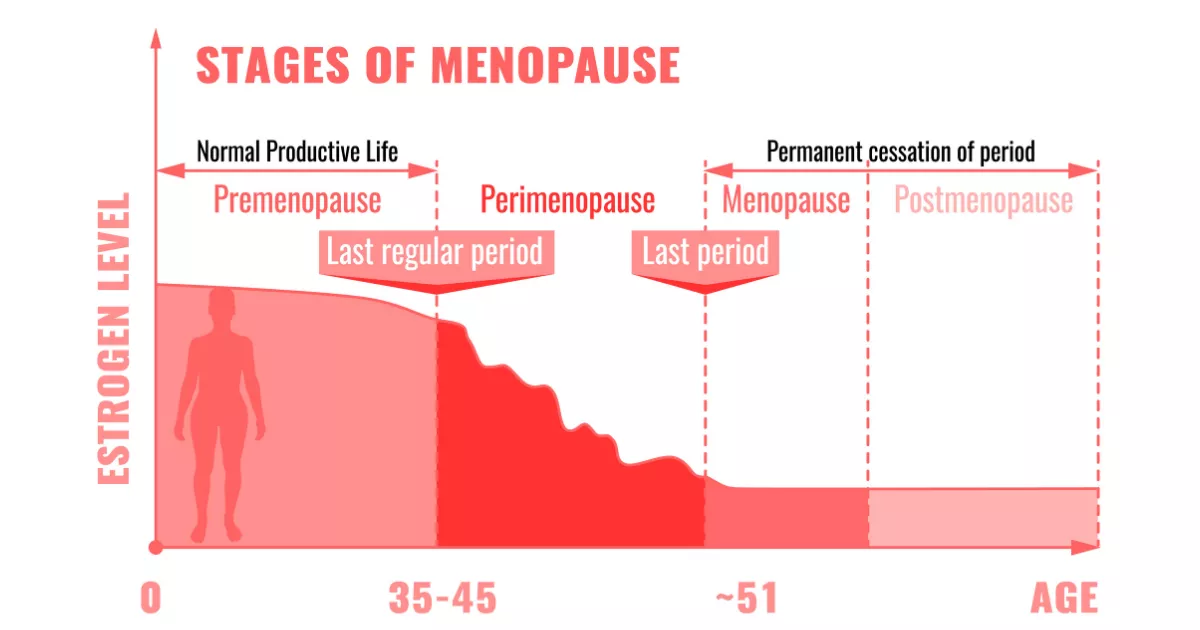
Menopause is a natural biological process that marks the end of a woman’s reproductive years. It occurs when the ovaries stop producing eggs and the levels of the hormones estrogen and progesterone decline. Menopause is a gradual process that can take several years to complete and is typically experienced by women between the ages of 45 and 55.
There are three main stages of menopause:
Perimenopause
Perimenopause is the transition period leading up to menopause. It can begin several years before menopause and is characterized by irregular menstrual cycles, hot flashes, night sweats, and other symptoms as the body adjusts to the declining levels of hormones.
Menopause
Menopause is the point at which a woman has not had a period for 12 consecutive months. This typically occurs between the ages of 45 and 55, but can vary depending on factors such as genetics, lifestyle, and overall health.
Postmenopause
Postmenopause is the period after menopause. During this stage, the levels of estrogen and progesterone remain low, and the risk of certain health conditions, such as osteoporosis and heart disease, increases.
Symptoms of Menopause
Menopause, a natural transition in a woman’s life, can manifest with a range of physical and emotional symptoms. These symptoms vary in severity and duration, affecting each woman differently. Understanding the common symptoms can help individuals prepare for and manage the changes associated with menopause.
Hot Flashes, How long does menopause last
Hot flashes are sudden feelings of intense heat, often accompanied by sweating, flushing, and palpitations. They can last from a few seconds to several minutes and occur frequently, particularly during the early stages of menopause. The severity of hot flashes can range from mild discomfort to debilitating.
Night Sweats
Night sweats are similar to hot flashes, but they occur during sleep. They can cause discomfort and disruption to sleep, leading to fatigue and irritability. Night sweats may be more severe than hot flashes during the day.
Vaginal Dryness
Menopause can lead to a decrease in estrogen levels, resulting in vaginal dryness. This can cause discomfort during sexual intercourse, burning, and itching. Vaginal dryness can also increase the risk of urinary tract infections.
Mood Changes
Hormonal changes during menopause can affect mood and emotions. Mood swings, irritability, anxiety, and depression are common symptoms. These changes can be mild or severe and may require professional support if they interfere with daily life.
Sleep Disturbances
Hot flashes, night sweats, and mood changes can disrupt sleep patterns during menopause. Difficulty falling asleep, staying asleep, and waking up feeling tired are common complaints. Sleep deprivation can exacerbate other symptoms of menopause.
Cognitive Changes
Some women may experience cognitive changes during menopause, including difficulty concentrating, forgetfulness, and decreased mental sharpness. These changes are usually mild and temporary, but they can be frustrating.
Other Symptoms
Other less common symptoms of menopause may include:
- Weight gain
- Hair loss
- Skin changes
- Joint pain
- Headaches
The severity and duration of menopause symptoms vary greatly from woman to woman. Some women experience only mild symptoms, while others may have more severe and persistent symptoms. Symptoms typically improve over time as hormone levels stabilize after menopause.
Managing Menopause
Managing menopause symptoms can be challenging, but various effective strategies are available. These include lifestyle modifications, hormone therapy, and alternative treatments. Understanding the benefits and risks associated with each approach is crucial for making informed decisions.
Lifestyle Modifications
Lifestyle modifications can significantly alleviate menopause symptoms. Maintaining a healthy weight, engaging in regular physical activity, and adopting a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can improve overall well-being and reduce the severity of symptoms like hot flashes and mood swings.
- Exercise:Regular exercise helps regulate body temperature, reduce stress, and improve sleep quality.
- Diet:Consuming a balanced diet rich in calcium, vitamin D, and phytoestrogens (plant-based compounds with estrogen-like effects) can help alleviate symptoms.
- Stress management:Techniques like yoga, meditation, and deep breathing can reduce stress and improve mood.
Hormone Therapy
Hormone therapy (HT) involves administering estrogen or a combination of estrogen and progestin to replenish the declining levels of these hormones during menopause. HT can effectively relieve hot flashes, night sweats, and vaginal dryness.
Benefits:
- Alleviates hot flashes and night sweats
- Prevents bone loss and reduces the risk of osteoporosis
- Improves vaginal health and reduces dryness
Risks:
- Increased risk of breast cancer (with long-term use)
- Increased risk of blood clots
li>Potential side effects like nausea, bloating, and headaches
Alternative Treatments
Alternative treatments, such as acupuncture, herbal remedies, and supplements, may provide additional support in managing menopause symptoms. However, it’s important to note that the efficacy and safety of these treatments may vary and should be discussed with a healthcare professional.
- Acupuncture:Acupuncture may help regulate hormones and reduce hot flashes and night sweats.
- Herbal remedies:Certain herbs, such as black cohosh and red clover, have been traditionally used to alleviate menopause symptoms.
- Supplements:Supplements like soy isoflavones and evening primrose oil may provide some relief from hot flashes and mood swings.
Impact of Menopause on Health
Menopause can have a significant impact on a woman’s overall health. These changes are primarily due to the decline in estrogen levels, which can affect various bodily systems. Understanding these potential effects and implementing strategies to mitigate them is crucial for maintaining health and well-being during this transition.
Cardiovascular Health
Menopause can increase the risk of cardiovascular disease, including heart attack and stroke. This is because estrogen has a protective effect on the heart and blood vessels. With declining estrogen levels, the risk of developing these conditions increases. To reduce this risk, it is important to maintain a healthy weight, exercise regularly, and follow a heart-healthy diet.
Additionally, quitting smoking and managing stress can further protect cardiovascular health.
Bone Density
Estrogen also plays a crucial role in maintaining bone density. After menopause, bone density decreases at an accelerated rate, increasing the risk of osteoporosis and fractures. Regular weight-bearing exercise, such as walking or running, and consuming a diet rich in calcium and vitamin D can help maintain bone strength.
Hormone replacement therapy (HRT) may also be an option to prevent bone loss in certain cases.
Mental Well-being
Menopause can also affect mental well-being. Mood swings, irritability, and anxiety are common symptoms. In some cases, more severe mental health issues, such as depression, can occur. Hormone replacement therapy (HRT) or other medications can be helpful in managing these symptoms.
Additionally, engaging in stress-reducing activities, such as yoga or meditation, and seeking support from friends, family, or a therapist can improve mental well-being during this transition.
Cultural and Social Aspects of Menopause
Menopause is a significant life event that can have a profound impact on women’s lives. The cultural and social perceptions of menopause vary widely around the world, and these perceptions can influence the experiences of women going through this transition.
Perception of Menopause in Different Cultures
In some cultures, menopause is seen as a time of wisdom and respect, while in others it is viewed as a time of decline and loss. In Western cultures, menopause is often associated with negative symptoms such as hot flashes, night sweats, and mood swings.
This can lead to women feeling embarrassed or ashamed of their experiences.
Influence on Women’s Experiences
The cultural and social perceptions of menopause can have a significant impact on the experiences of women going through this transition. Women who live in cultures where menopause is viewed positively may be more likely to have a positive experience, while those who live in cultures where menopause is viewed negatively may be more likely to experience negative symptoms.
Importance of Cultural Sensitivity
It is important for healthcare providers to be aware of the cultural and social perceptions of menopause when providing care to women going through this transition. By understanding the cultural context of a woman’s experience, healthcare providers can provide more culturally sensitive and supportive care.
Menopause in Different Populations
The experience of menopause can vary significantly among different populations, influenced by factors such as race, ethnicity, socioeconomic background, and cultural beliefs.
Socioeconomic factors, such as education, income, and access to healthcare, can impact the timing and severity of menopausal symptoms. Women with higher socioeconomic status tend to experience menopause later and have milder symptoms compared to women with lower socioeconomic status.
Race and Ethnicity
Racial and ethnic differences also play a role in menopausal experiences. For instance, African American women tend to enter menopause earlier than white women, while Asian women generally experience menopause later.
Furthermore, cultural beliefs and practices can shape the perception and management of menopause. In some cultures, menopause is viewed as a natural transition, while in others, it is seen as a time of decline or loss.
Future Directions in Menopause Research

Menopause research is a rapidly evolving field, with numerous emerging trends and future directions that hold promise for improving our understanding and management of this transition.
One key area of focus is the role of epigenetics in menopause. Epigenetics refers to the study of how environmental factors can influence gene expression without altering the DNA sequence itself. Research in this area is exploring how lifestyle factors, such as diet and exercise, can affect the timing and symptoms of menopause.
Precision Medicine
Another emerging trend is the development of precision medicine approaches to menopause management. Precision medicine aims to tailor treatments to the individual characteristics of each patient, based on their genetic makeup, lifestyle, and other factors. This approach has the potential to improve the effectiveness and reduce the side effects of menopause treatments.
Technology
Technology is also playing an increasingly important role in menopause research. The development of wearable devices and other technologies is enabling researchers to collect more objective data on menopause symptoms, such as hot flashes and sleep disturbances. This data can help to identify patterns and develop more effective interventions.
FAQ Summary: How Long Does Menopause Last
What is the average duration of menopause?
Menopause typically lasts between 4 and 8 years, but it can vary significantly from woman to woman.
What factors can influence the length of menopause?
Age, lifestyle, and certain health conditions can all impact the duration of menopause.
What are the stages of menopause?
Menopause has three stages: perimenopause, menopause, and postmenopause.
How can I manage menopause symptoms?
Lifestyle modifications, hormone therapy, and alternative treatments can all help manage menopause symptoms.
What is the impact of menopause on health?
Menopause can have a significant impact on cardiovascular health, bone density, and mental well-being.