When does menopause start? This question marks the onset of a significant biological transition for women, signaling the end of their reproductive years. As we delve into this topic, we will explore the intricate processes, symptoms, and implications associated with menopause, empowering you with the knowledge to navigate this transformative phase with confidence.
Menopause is a natural process that typically occurs between the ages of 45 and 55. However, factors such as genetics and lifestyle can influence the age of onset, making it a highly individualized experience. Understanding the average age of onset and the factors that may affect it is crucial for women to plan and prepare for this transition.
Average Age of Onset
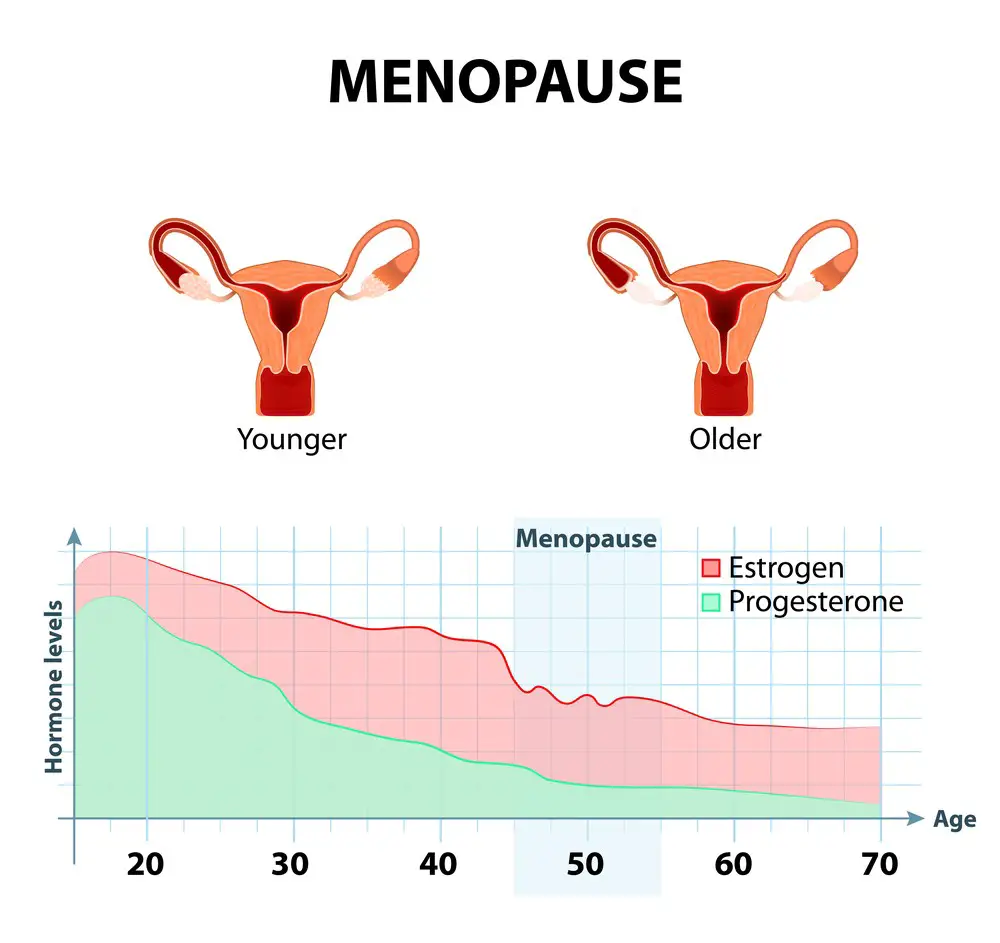
Menopause typically begins between the ages of 45 and 55, with an average age of 51 in the United States. However, the age of onset can vary significantly from person to person.
Factors Influencing Age of Onset
Several factors can influence the age at which a woman experiences menopause, including:
- Genetics:Women with a family history of early menopause are more likely to experience it at an earlier age.
- Lifestyle:Certain lifestyle factors, such as smoking and obesity, can contribute to earlier menopause.
- Medical conditions:Certain medical conditions, such as autoimmune disorders and thyroid disease, can also affect the age of menopause.
Symptoms and Signs
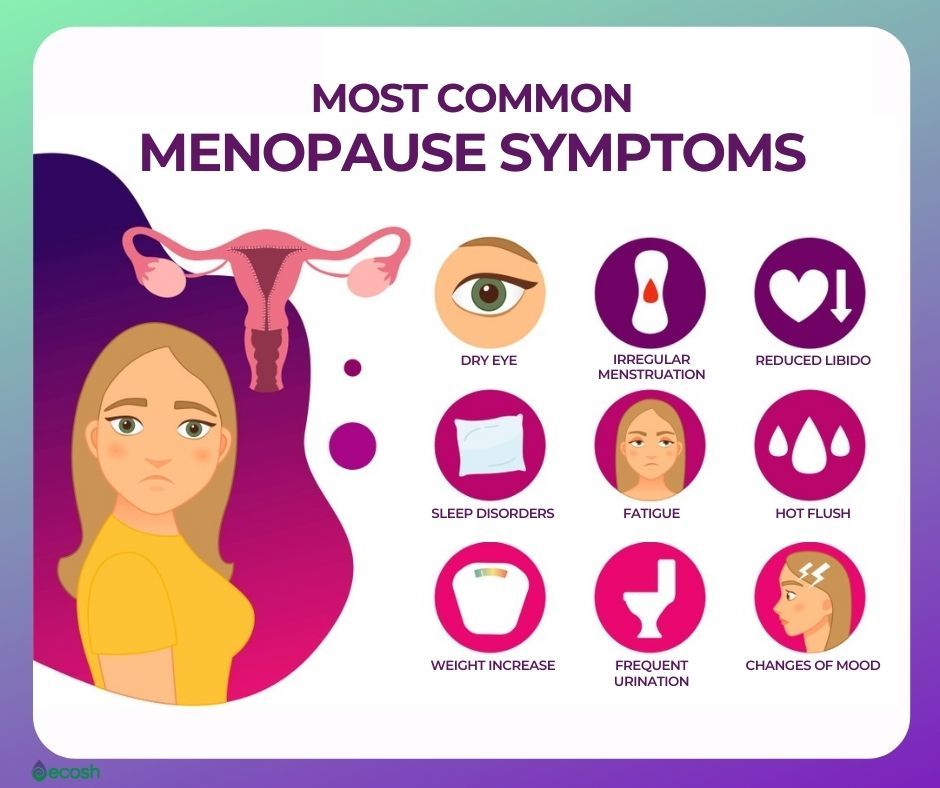
Menopause is characterized by a range of physical and emotional symptoms that arise due to the hormonal changes associated with the cessation of menstrual cycles.
These changes primarily involve a decline in estrogen and progesterone levels, which can lead to:
Physical Symptoms
- Hot flashes and night sweats
- Vaginal dryness and discomfort
- Difficulty sleeping
- Changes in mood and irritability
- Loss of bone density (osteoporosis)
- Increased risk of heart disease and stroke
Emotional Symptoms
- Anxiety and depression
- Mood swings
- Difficulty concentrating
- Loss of interest in activities
- Increased risk of cognitive decline
Stages of Menopause
Menopause is a natural process that marks the end of a woman’s reproductive years. It occurs when the ovaries stop producing eggs and the levels of the hormones estrogen and progesterone decline.
Menopause typically occurs between the ages of 45 and 55, but it can happen earlier or later. The transition to menopause is a gradual process that can take several years and is divided into three stages:
Perimenopause
Perimenopause is the stage that begins several years before menopause and ends when a woman has not had a period for 12 consecutive months. During this stage, the ovaries gradually produce less estrogen and progesterone, which can cause a variety of symptoms, including:
- Irregular periods
- Hot flashes
- Night sweats
- Sleep disturbances
- Mood swings
- Vaginal dryness
- Weight gain
Menopause
Menopause is the point in time when a woman has not had a period for 12 consecutive months. The ovaries have stopped producing eggs, and the levels of estrogen and progesterone are very low.
The symptoms of menopause can vary from woman to woman, but they typically include:
- Hot flashes
- Night sweats
- Sleep disturbances
- Mood swings
- Vaginal dryness
- Weight gain
- Osteoporosis
Postmenopause
Postmenopause is the stage that begins after menopause and lasts for the rest of a woman’s life. During this stage, the levels of estrogen and progesterone remain low, and the symptoms of menopause gradually subside.
However, some women may continue to experience some symptoms of menopause, such as hot flashes, night sweats, and vaginal dryness. Postmenopausal women are also at an increased risk for osteoporosis and heart disease.
Treatment Options
Menopause can bring a range of uncomfortable symptoms that can impact a woman’s daily life. Fortunately, various treatment options are available to manage these symptoms and improve overall well-being during this transition.
Hormone Replacement Therapy (HRT), When does menopause start
HRT is a common treatment option that involves taking hormones, such as estrogen and progesterone, to replace the hormones that the body stops producing during menopause. HRT can effectively alleviate many menopausal symptoms, including hot flashes, night sweats, vaginal dryness, and mood changes.
However, HRT also carries potential risks, such as an increased risk of breast cancer, blood clots, and stroke. It is essential to discuss the benefits and risks of HRT with a healthcare professional to determine if it is the right treatment option for you.
Non-Hormonal Medications
Several non-hormonal medications are available to treat specific menopausal symptoms. For example, antidepressants can help alleviate mood swings and anxiety, while vaginal moisturizers can address vaginal dryness.
Lifestyle Modifications
Making certain lifestyle changes can also help manage menopausal symptoms. These include:
- Maintaining a healthy weight
- Eating a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains
- Getting regular exercise
- Managing stress
- Quitting smoking
- Limiting alcohol consumption
By implementing these lifestyle changes, women can reduce the severity of their symptoms and improve their overall health during menopause.
Alternative Therapies
Some women find relief from menopausal symptoms through alternative therapies, such as acupuncture, herbal remedies, or yoga. While these therapies may not be scientifically proven to be effective, they may provide some symptomatic relief for certain individuals.It is important to note that every woman’s experience with menopause is unique, and the best treatment approach will vary depending on individual symptoms and preferences.
It is always advisable to consult with a healthcare professional to discuss the most appropriate treatment options for you.
Lifestyle Modifications
Lifestyle modifications play a significant role in managing menopause symptoms and improving overall well-being during this transition. By adopting certain changes in daily routine, individuals can effectively alleviate the physical and emotional challenges associated with menopause.
Incorporating regular exercise, adopting a balanced diet, and implementing stress management techniques are key aspects of lifestyle modifications for menopause management.
Exercise
Engaging in regular physical activity can significantly alleviate various menopause symptoms. Exercise helps reduce hot flashes, improve sleep quality, boost mood, and strengthen bones. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise most days of the week.
Diet
Maintaining a healthy diet during menopause is essential. Consuming fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein helps regulate hormone levels, reduce inflammation, and improve overall health. Limit processed foods, sugary drinks, and unhealthy fats, as they can worsen symptoms.
Stress Management
Stress can exacerbate menopause symptoms. Incorporating stress management techniques into daily routine can help reduce anxiety, improve sleep, and alleviate mood swings. Consider activities such as yoga, meditation, or spending time in nature to promote relaxation and stress reduction.
Impact on Health

Menopause marks a significant transition in a woman’s life, not only physically but also in terms of overall health. As the body adjusts to hormonal changes, it may experience an increased risk of developing certain health conditions.
One of the most significant health implications associated with menopause is osteoporosis, a condition that weakens bones and makes them more susceptible to fractures. This occurs due to the decline in estrogen levels, which play a crucial role in maintaining bone density.
As a result, women in menopause are at an increased risk of developing osteoporosis, particularly in the years immediately following menopause.
Cardiovascular Disease
Menopause can also increase the risk of cardiovascular disease, including heart disease and stroke. The decline in estrogen levels can lead to changes in blood vessel function, increasing the risk of plaque buildup and narrowing of the arteries. Additionally, changes in cholesterol levels and weight gain during menopause can further contribute to the development of cardiovascular disease.
Other Conditions
Menopause can also increase the risk of developing other health conditions, such as:
- Urinary incontinence: Weakening of the pelvic floor muscles due to hormonal changes can lead to difficulty controlling urination.
- Vaginal dryness: Reduced estrogen levels can cause thinning and dryness of the vaginal tissues, leading to discomfort during intercourse and an increased risk of vaginal infections.
- Cognitive decline: While the link between menopause and cognitive decline is still being studied, some research suggests that women in menopause may experience a slight decline in memory and other cognitive functions.
- Mood changes: Fluctuating hormone levels during menopause can contribute to mood swings, irritability, and anxiety.
Social and Cultural Aspects: When Does Menopause Start
The experience of menopause is influenced by various social and cultural factors. Societal attitudes and expectations can impact women’s perception and management of menopausal symptoms and their overall well-being during this transition.
Impact of Societal Attitudes
In many cultures, menopause is often associated with negative stereotypes and perceived as a time of decline or loss. These attitudes can lead to feelings of shame, embarrassment, or isolation among women going through menopause.
Societal expectations of women’s roles and responsibilities can also influence their experience of menopause. In some cultures, women may be expected to continue fulfilling traditional roles as caregivers and household managers, despite experiencing menopausal symptoms that can make these tasks challenging.
Influence of Cultural Beliefs and Practices
Cultural beliefs and practices can shape how women perceive and manage menopause. In some cultures, menopause is seen as a natural and honored transition, while in others, it may be considered a time of illness or weakness.
Traditional remedies and practices may be used to address menopausal symptoms, such as herbal teas, acupuncture, or massage therapy. These practices can provide support and comfort, but it’s important to consult with healthcare professionals to ensure their safety and effectiveness.
FAQ Compilation
What are the common symptoms of menopause?
Menopause symptoms can vary widely but commonly include hot flashes, night sweats, vaginal dryness, mood swings, and sleep disturbances.
What causes menopause?
Menopause is caused by a decline in the production of estrogen and progesterone, which are hormones produced by the ovaries.
Can menopause be prevented?
Menopause is a natural process that cannot be prevented. However, lifestyle factors such as maintaining a healthy weight, exercising regularly, and managing stress can help alleviate symptoms.