Menopause questions often shroud women in a veil of uncertainty, leaving them grappling with physical, emotional, and social transitions. Embark on this enlightening journey as we unravel the complexities of menopause, empowering you with knowledge and support.
This comprehensive guide delves into the myriad of symptoms, treatment options, health risks, and emotional challenges associated with menopause. We explore the impact of hormonal fluctuations on well-being, sexual health, and societal perceptions, providing practical strategies for navigating this transformative phase.
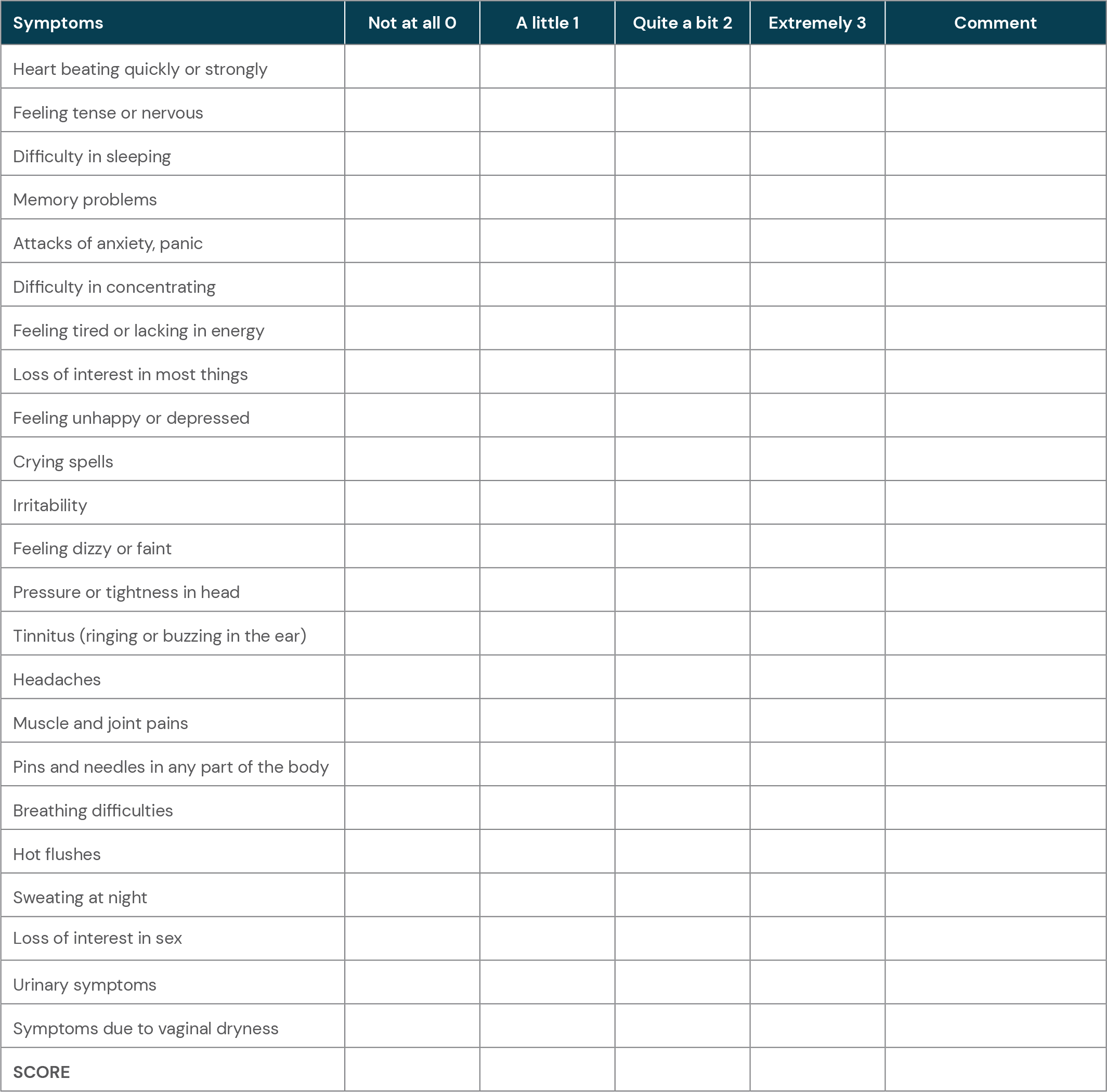
Menopause Symptoms
Menopause is a natural transition in a woman’s life, marked by the cessation of menstruation and a decline in reproductive hormones, primarily estrogen and progesterone. This hormonal shift triggers a range of physical and emotional symptoms that can vary in severity and duration from woman to woman.
Physical Symptoms
- Hot flashes: Sudden feelings of intense heat and sweating, often accompanied by redness of the face, neck, and chest. These episodes can be unpredictable and occur multiple times a day, lasting for several minutes to hours.
- Night sweats: Hot flashes that occur during sleep, leading to disrupted sleep patterns and fatigue.
- Vaginal dryness: Decreased estrogen levels cause the vaginal tissues to become thinner, drier, and less elastic, resulting in discomfort during intercourse and an increased risk of urinary tract infections.
- Osteoporosis: Reduced estrogen levels weaken bones, making them more susceptible to fractures and osteoporosis.
- Weight gain: Hormonal changes can affect metabolism and lead to weight gain, particularly around the abdomen.
Emotional Symptoms
- Mood swings: Fluctuating hormone levels can cause irritability, anxiety, depression, and mood swings.
- Sleep disturbances: Hot flashes, night sweats, and hormonal changes can disrupt sleep, leading to fatigue and difficulty concentrating.
- Cognitive changes: Some women may experience mild cognitive changes, such as difficulty with memory, focus, and attention.
Menopause Treatment Options
Menopause symptoms can significantly impact women’s quality of life. Various treatment options are available to manage these symptoms and improve well-being during this transition.
Hormone Replacement Therapy (HRT)
HRT involves administering synthetic hormones, estrogen, and progesterone, to replace the declining levels during menopause. It effectively alleviates vasomotor symptoms (hot flashes and night sweats) and can also prevent bone loss.
Mechanism of Action:HRT replenishes estrogen and progesterone, mimicking the body’s natural hormone production, thus reducing the symptoms associated with their deficiency.
Benefits:
- Relieves hot flashes and night sweats
- Prevents bone loss and reduces the risk of osteoporosis
- Improves sleep quality
- May alleviate vaginal dryness and urinary incontinence
Side Effects:
- Breast tenderness
- Nausea
- Bloating
- Increased risk of blood clots and stroke in certain individuals
Menopause and Health Risks: Menopause Questions

Menopause is a natural transition in a woman’s life, but it can also bring about an increased risk of certain health conditions. These include osteoporosis, heart disease, and dementia.
During menopause, the body undergoes hormonal changes that can affect bone density, cardiovascular health, and cognitive function. For instance, the decline in estrogen levels can lead to bone loss, increasing the risk of osteoporosis. Additionally, the changes in hormone levels can affect cholesterol levels and blood pressure, contributing to the increased risk of heart disease.
Osteoporosis
- Osteoporosis is a condition that causes bones to become weak and brittle, making them more susceptible to fractures.
- The decline in estrogen levels during menopause can lead to increased bone loss, as estrogen plays a role in maintaining bone density.
- Strategies for reducing the risk of osteoporosis include getting regular exercise, maintaining a healthy weight, and consuming a diet rich in calcium and vitamin D.
- Medical interventions such as hormone replacement therapy or bisphosphonates may also be considered to prevent or treat osteoporosis.
Heart Disease
- Heart disease is the leading cause of death among women in the United States.
- Menopause can increase the risk of heart disease due to changes in hormone levels, which can affect cholesterol levels and blood pressure.
- Strategies for reducing the risk of heart disease include maintaining a healthy weight, exercising regularly, eating a heart-healthy diet, and managing stress.
- Medical interventions such as statins or blood pressure medications may also be necessary to reduce the risk of heart disease.
Dementia
- Dementia is a decline in cognitive function that can affect memory, thinking, and reasoning.
- While the exact cause of dementia is not fully understood, research suggests that hormonal changes during menopause may play a role.
- Strategies for reducing the risk of dementia include staying mentally active, exercising regularly, and eating a healthy diet.
- Medical interventions such as hormone replacement therapy or cholinesterase inhibitors may also be considered to prevent or treat dementia.
Menopause and Emotional Well-being

Menopause is a time of significant hormonal changes that can impact a woman’s emotional well-being. Fluctuating levels of estrogen and progesterone can lead to a range of emotional challenges, including mood swings, anxiety, and depression.
Hormonal Fluctuations and Emotional Changes
Estrogen and progesterone are hormones that play crucial roles in regulating mood and behavior. During menopause, levels of these hormones decline, which can disrupt the brain’s neurochemistry and lead to emotional instability. Decreased estrogen levels have been linked to mood swings, irritability, and difficulty concentrating.
Progesterone, on the other hand, has calming effects and its decline can contribute to anxiety and depression.
Coping with Emotional Well-being during Menopause
While the emotional challenges of menopause can be significant, there are effective strategies for coping with them:
Engage in regular exercise
Physical activity releases endorphins, which have mood-boosting effects.
Maintain a healthy diet
Eating a balanced diet that includes plenty of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can help improve overall health and well-being.
Get enough sleep
Sleep deprivation can worsen mood swings and anxiety. Aim for 7-9 hours of sleep each night.
Practice stress-reducing techniques
Engage in activities such as yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises to manage stress and improve emotional well-being.
Seek professional help if needed
If emotional symptoms are severe or persistent, do not hesitate to consult a healthcare professional. Therapy or medication may be necessary to address underlying mental health issues.
Menopause and Social Implications
Menopause is often shrouded in social and cultural perceptions that can significantly impact women’s experiences and self-image. These perceptions vary across cultures and societies, shaping how women perceive and cope with the physical, emotional, and social changes associated with menopause.
In many societies, menopause is viewed as a time of decline, loss of fertility, and diminished value. This negative perception can lead to stigma, discrimination, and social isolation, affecting women’s self-esteem and overall well-being.
Challenging Societal Stigma, Menopause questions
- Promote Education and Awareness:Educate the public about menopause, its symptoms, and the importance of supporting women during this transition. This can help dispel myths and misconceptions and foster a more informed and understanding society.
- Encourage Open Dialogue:Create platforms for women to share their experiences and perspectives on menopause. This can help normalize the conversation and reduce the sense of isolation and shame often associated with it.
- Support Advocacy Groups:Empower women by supporting advocacy groups that work to promote positive attitudes towards menopause and advocate for policies that protect women’s rights and well-being during this stage of life.
- Challenge Stereotypes in Media:Challenge the portrayal of menopause in the media, which often perpetuates negative stereotypes and reinforces societal biases. Instead, promote positive and realistic representations that reflect the diverse experiences of women going through menopause.
Promoting Positive Attitudes
- Celebrate the Transition:Encourage women to view menopause as a natural transition and an opportunity for personal growth and empowerment. This can help shift the focus away from loss and towards the potential for new beginnings.
- Foster Intergenerational Support:Connect women of different generations to share experiences and offer support. This can help break down barriers and promote understanding between women at different stages of life.
- Encourage Self-Care and Empowerment:Empower women to prioritize their health and well-being during menopause. Encourage them to engage in activities that promote physical, emotional, and mental health, such as exercise, healthy eating, and stress management techniques.
- Promote Respect and Inclusion:Encourage respectful and inclusive attitudes towards women going through menopause. This includes valuing their contributions, recognizing their experiences, and ensuring they feel supported and respected in all aspects of life.
Menopause and Nutrition
Menopause marks a significant hormonal shift in a woman’s life, affecting various aspects of her health, including nutritional needs. During this transition, women experience decreased estrogen levels, which can impact bone density, metabolism, and overall well-being. To navigate these changes effectively, it is essential to adopt a nutrient-rich diet that supports the body’s changing requirements.
Nutritional Needs and Dietary Recommendations
During menopause, women have increased nutritional needs for certain vitamins, minerals, and other nutrients. These include:
-
-*Calcium
Essential for maintaining bone health and preventing osteoporosis, which becomes a concern with declining estrogen levels.
-*Vitamin D
Aids in calcium absorption and bone health.
-*Phytoestrogens
Plant-based compounds that have estrogen-like effects, potentially alleviating menopausal symptoms.
-*Omega-3 fatty acids
Support heart health and reduce inflammation, which can be beneficial during menopause.
-*Fiber
Promotes digestive health and helps regulate blood sugar levels.
-*Antioxidants
Protect cells from damage caused by free radicals, which can contribute to aging and disease.
Incorporating these nutrients into a balanced diet can help manage menopausal symptoms, maintain overall health, and reduce the risk of chronic diseases.
Role of Specific Nutrients
Calcium and Vitamin D:Calcium is crucial for maintaining bone density and preventing osteoporosis. During menopause, women lose bone mass at an accelerated rate, increasing their risk of fractures. Vitamin D enhances calcium absorption, further supporting bone health.Phytoestrogens:Phytoestrogens, found in plant foods like soybeans, tofu, and flaxseed, have weak estrogenic activity.
They may help alleviate menopausal symptoms such as hot flashes and vaginal dryness by binding to estrogen receptors in the body.Omega-3 Fatty Acids:Omega-3 fatty acids, found in fish, walnuts, and flaxseed, have anti-inflammatory properties. They may reduce inflammation associated with menopause and improve heart health.
Menopause and Exercise
Regular exercise is crucial for managing menopause symptoms and improving overall health. It helps reduce hot flashes, improves mood, and maintains bone health.
Exercise Recommendations for Women During Menopause
Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic activity per week. Include strength-training exercises two or more days per week.
- Aerobic activities:Walking, running, swimming, cycling, dancing
- Strength-training exercises:Resistance bands, weights, bodyweight exercises
Benefits of Exercise During Menopause
- Reduced hot flashes:Exercise increases blood flow and circulation, which can help regulate body temperature.
- Improved mood:Exercise releases endorphins, which have mood-boosting effects.
- Maintained bone health:Weight-bearing exercises help build and maintain bone density, reducing the risk of osteoporosis.
Key Questions Answered
What are the common physical symptoms of menopause?
Hot flashes, night sweats, vaginal dryness, sleep disturbances, and weight gain are some prevalent physical symptoms.
How can I manage hot flashes during menopause?
Lifestyle modifications such as wearing loose clothing, using cooling fans, and practicing relaxation techniques can help alleviate hot flashes.
What are the emotional challenges associated with menopause?
Mood swings, anxiety, depression, and irritability are common emotional experiences during menopause due to hormonal fluctuations.
How does menopause affect sexual health?
Menopause can lead to decreased libido, vaginal dryness, and painful intercourse due to declining estrogen levels.
What dietary recommendations are beneficial during menopause?
A balanced diet rich in calcium, vitamin D, and phytoestrogens is recommended to support bone health and manage menopause symptoms.