Hot flashes symptoms, a common experience during menopause, can significantly impact daily life. Understanding these symptoms, their triggers, and available management strategies is crucial for maintaining well-being during this transition.
Hot flashes manifest as sudden sensations of intense heat accompanied by sweating, heart palpitations, and anxiety. These symptoms can disrupt sleep, impair concentration, and affect mood, leading to diminished quality of life.
Definition of Hot Flashes
Hot flashes are a common symptom of menopause, a period of transition in a woman’s life when their menstrual periods stop and their ovaries stop producing eggs. Hot flashes are characterized by a sudden feeling of heat that spreads over the body, often accompanied by sweating, flushing, and a rapid heart rate.
Physiological Mechanisms, Hot flashes symptoms
Hot flashes occur due to changes in the body’s temperature regulation system. During menopause, the levels of the hormone estrogen decline, which can lead to fluctuations in body temperature. These fluctuations can trigger the body’s “thermostat” to malfunction, resulting in hot flashes.
Prevalence and Occurrence
Hot flashes are a common experience during menopause, affecting up to 85% of women. They typically begin within the first few years after menopause and can last for several years. The frequency and severity of hot flashes can vary from woman to woman.
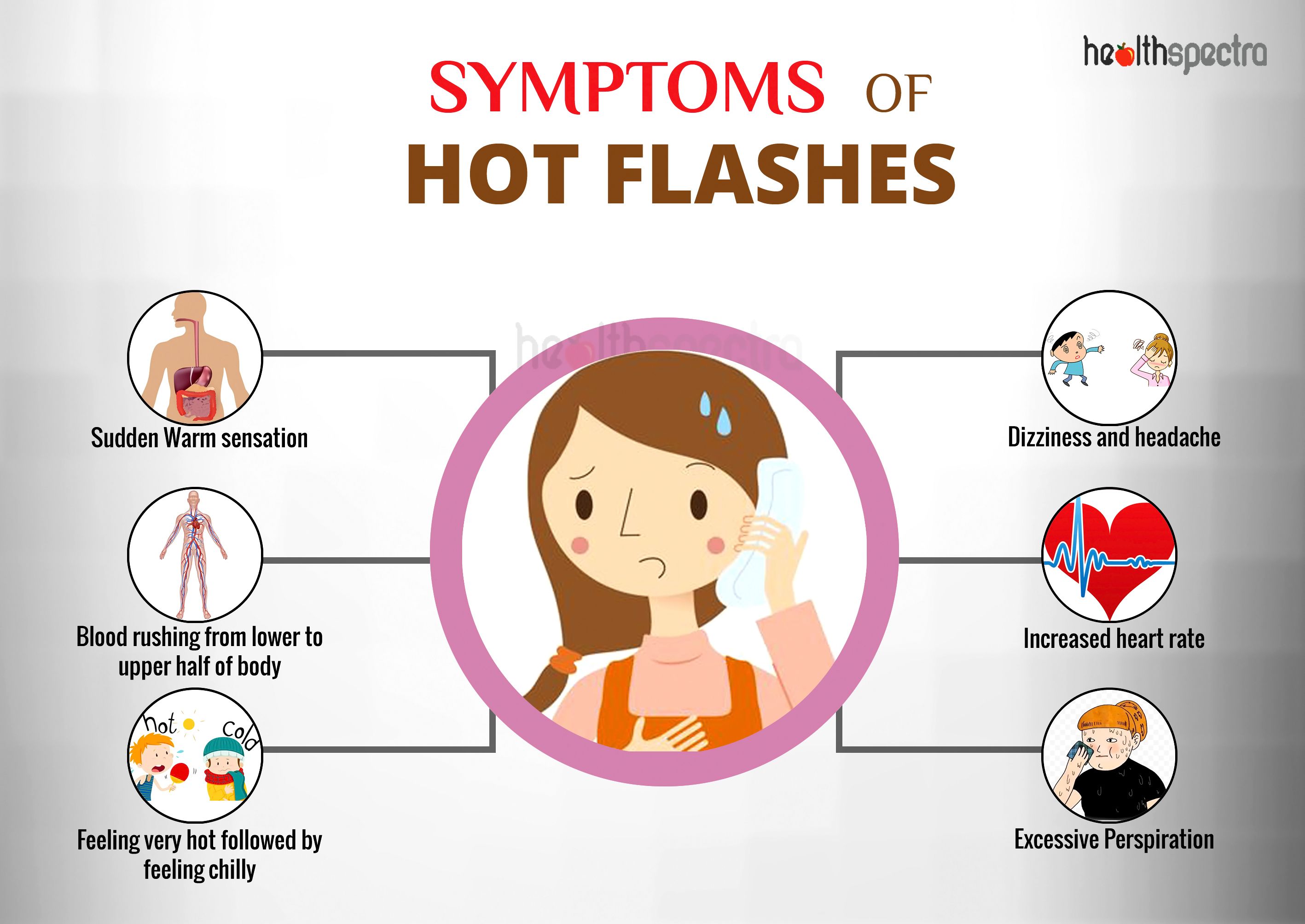
Symptoms Associated with Hot Flashes

Hot flashes are sudden episodes of intense heat that typically last for a few minutes. They are a common symptom of menopause, but can also occur during other times of hormonal change, such as during pregnancy, breastfeeding, or when taking certain medications.
Hot flashes can cause a range of physical and emotional symptoms, which can vary in severity from person to person.
Physiological symptomsof hot flashes include:
- Sweating
- Heart palpitations
- Flushing
- Chills
- Nausea
- Headache
- Dizziness
- Fatigue
Psychological symptomsof hot flashes include:
- Anxiety
- Irritability
- Mood swings
- Difficulty concentrating
- Sleep disturbances
Hot flashes can be a disruptive and uncomfortable experience, but there are a number of things that can be done to manage them, including lifestyle changes, medications, and alternative therapies.
Triggers and Causes of Hot Flashes
Hot flashes are primarily triggered by hormonal changes associated with menopause, particularly the decline in estrogen levels. This hormonal imbalance affects the body’s thermoregulatory system, causing it to overreact to slight changes in temperature.
Besides hormonal fluctuations, certain lifestyle factors and medical conditions can also contribute to hot flashes:
Lifestyle Factors
- Stress and anxiety
- Caffeine and alcohol consumption
- Spicy foods
- Smoking
- Lack of sleep
Medical Conditions
- Thyroid disorders
- Certain medications, such as antidepressants and steroids
- Diabetes
- Cancer treatments, such as chemotherapy and radiation therapy
Understanding the triggers and causes of hot flashes can help women develop strategies to manage and reduce their frequency and severity.
Impact of Hot Flashes on Daily Life

Hot flashes can significantly impact daily life, affecting sleep quality, mood, and social interactions. The sudden and intense heat sensations can disrupt daily activities, leading to discomfort and distress.
Sleep Disturbances
- Hot flashes can cause night sweats and sleep disturbances, leading to fatigue and impaired daytime functioning.
- Interrupted sleep can also worsen mood and increase irritability.
Mood Changes
- Hot flashes can trigger mood swings, anxiety, and irritability.
- The unpredictable nature of hot flashes can lead to feelings of frustration and embarrassment.
Social Interactions
- Hot flashes can cause discomfort and embarrassment in social situations.
- People may avoid social interactions or feel self-conscious about their symptoms.
Management and Treatment Options
Managing hot flashes can involve a combination of lifestyle modifications and medical treatments. Understanding the triggers and causes of hot flashes can help individuals tailor their management strategies.
Lifestyle Modifications
Certain lifestyle changes can help reduce the frequency and severity of hot flashes:
- Dietary Changes:Avoiding spicy foods, caffeine, and alcohol can help reduce triggers.
- Exercise:Regular exercise helps regulate body temperature and reduce stress levels.
- Stress Reduction Techniques:Relaxation techniques like yoga, meditation, and deep breathing can help manage stress, which can trigger hot flashes.
Medical Treatments
In some cases, medical treatments may be necessary to manage hot flashes effectively:
- Hormone Replacement Therapy (HRT):HRT involves taking hormones like estrogen or progesterone to replace the hormones lost during menopause.
- Antidepressants:Certain antidepressants, such as venlafaxine and paroxetine, can help reduce hot flash frequency and severity.
- Natural Remedies:Some herbal remedies, such as black cohosh and red clover, have been shown to have some benefits in reducing hot flashes.
Coping Mechanisms and Support: Hot Flashes Symptoms
Managing hot flashes can be challenging, but there are effective coping mechanisms and support systems available. Understanding these strategies can empower individuals to navigate this experience with confidence.
Practical coping mechanisms include:
In Public Settings
- Carry a portable fan or misting device.
- Wear loose, breathable clothing made from natural fibers.
- Find a cool spot to sit or stand when possible.
- Take deep breaths to calm the body.
- Sip on cold water or juice to regulate body temperature.
In Private Settings
- Take a cool shower or bath.
- Apply a cold compress to the face or neck.
- Use a fan or air conditioner to cool the room.
- Wear lightweight, moisture-wicking sleepwear.
- Elevate the head and shoulders while sleeping to promote circulation.
In addition to coping mechanisms, support groups and online forums provide a sense of community and shared experiences. These platforms offer a safe space to connect with others who understand the challenges of hot flashes and provide emotional support and practical advice.
FAQ Overview
What are the common physical symptoms of hot flashes?
Physical symptoms include sweating, heart palpitations, facial flushing, and chills.
Can hot flashes cause emotional symptoms?
Yes, hot flashes can trigger anxiety, irritability, and mood swings.
What lifestyle changes can help manage hot flashes?
Stress reduction techniques, regular exercise, and dietary modifications can alleviate hot flash severity.